Hearing Aid
Hearing Aid
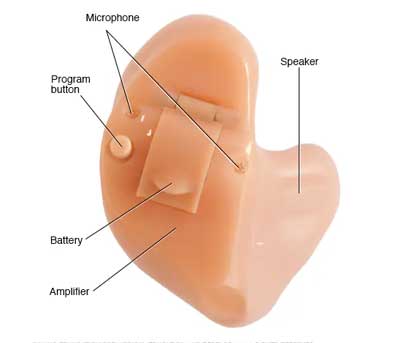
All hearing aids use the same basic parts to carry sounds from the environment into your ear and make them louder. Most hearing aids are digital, and all are powered with a traditional hearing aid battery or a rechargeable battery.
Small microphones collect sounds from the environment. A computer chip with an amplifier converts the incoming sound into digital code. It analyzes and adjusts the sound based on your hearing loss, listening needs and the level of the sounds around you. The amplified signals are then converted back into sound waves and delivered to your ears through speakers, sometimes called receivers.